Islamic vs Conventional Bonds, How Are The Two Different?
Bonds are divided into 2 types based on the principles used, namely sharia and conventional. What exactly is the difference between Islamic bonds and conventional bonds?
Bonds are one of the investment alternatives that people love to choose. This asset is considered as an investment asset that has a small risk value. In addition, profits in the form of coupons are a sign that this type of investment has a more constant income compared to other types of investments stock investment.
In general, bonds are defined as securities issued by the government or companies that usually mature in the long term (more than one year). Bonds have various types. However, basically, bonds are divided into 2 types with different properties, namely conventional bonds and Islamic bonds or often referred to as sukuk.
Are you interested in investing in bonds and curious about these two types of bond instruments? What exactly is the difference between Islamic bonds and conventional bonds? The following is an explanation of Islamic bonds, conventional bonds, and the differences between the two.
Conventional Bonds

General bonds or conventional bonds are often chosen by investors as an alternative investment because the risks are relatively small and the income in the form of coupons or interest is obtained regularly. What exactly is this conventional bond? The following is the definition and types of conventional bonds.
Definition of Conventional Bonds
Conventional bonds or general bonds are securities in the form of debt securities issued by both the government and companies.
In bonds, there are two main parties that make transactions, namely the government or the issuing company which acts as the party that borrows funds or the debtor. Meanwhile, there are bondholders who act as lenders of funds or creditors.
The main purpose of the issuance of bonds type securities in general is so that debtors get capital to use funding long-term. Meanwhile, the benefits of investing in bonds for investors are in the form of interest that is obtained regularly and the amount is certain.
Conventional Bond Type
Conventional bonds have various types with certain classifications. These securities can be distinguished based on the issuer, payment system, right of exchange, the existence of a guarantee. The following are the types of conventional bonds.
Types of Bonds by Issuer
Based on the issuer, bonds can be divided into the following types.
- government bond; are bonds issued by the government. Examples of these bonds in Indonesia are Indonesian Retail Bonds (ORI), Government Bonds (SUN).
- corporate bonds; which are bonds issued by the company as a source of external funding for the company.
- municipal bond; are bonds issued by local governments.
Types of Bonds Based on Right of Exchange
Based on the right of redemption, bonds can be divided into the following types.
- Convertible bonds; are bonds that can be exchanged for shares issued by the bond issuer
- Exchangeable bonds; exchangeable bonds has a meaning that is almost similar to convertible bonds where bonds can be exchanged for stocks, the difference exchangeable bonds can be exchanged for affiliated shares of the issuing company.
- Callable bonds; namely bonds that give the bond issuer the right to buy back the bonds at a certain price before the bond matures.
- putable bonds; bonds in which it gives the bondholder the right to be able to sell or request settlement from the bond issuer.
Types of Bonds Based on Collateral
Based on the collateral, bonds can be divided into the following types.
- secure bonds; is a bond whose settlement is guaranteed by certain assets by the issuer
- Guaranteed bonds; namely bonds guaranteed by third parties
- Mortgage bonds; mortgage bonds is a bond whose repayment is guaranteed by certain property (usually a building)
- Collateral trust bonds; i.e. bonds guaranteed by financial assets in, for example, company shares
- Unsecured bonds; i.e. bonds that are not guaranteed by any asset or property
Types of Bonds Based on Payment System
Based on the payment system, bonds can be divided into the following types.
- Zero coupon bonds; is a bond in which there is no obligation for the issuer to pay coupons or interest to the bond owner
- Coupon bonds; namely bonds that provide an obligation for bond issuers to provide yields in the form of interest to bondholders either in the form of fixed interest (fixed coupon bonds) and floating bond interest (floating coupon bonds)
Sharia Bonds

Sukuk or what can be referred to as Islamic bonds are one of the investment alternatives that are widely chosen by the public. What exactly is this Sharia Bond? The following is the definition of Islamic bonds and the types of these assets.
Definition of Sharia Bonds
Bond sharia is one of the securities in the form of a certificate or proof of ownership with a yield in the form of rent (ujrah) with a certain percentage.
Unlike conventional bonds or bonds in general, Islamic bonds are not in the form of debt securities and the yield is not in the form of interest. Sukuk or sharia bonds will be guided by Islamic laws which tend to avoid usury.
So, Islamic bonds are in the form of certificates of ownership and the yield is in the form of rent. Even so, Islamic bonds still have properties like other bonds in which the return on this investment will be paid regularly and the principal value of the loan will also be paid when the asset matures.
In addition, just like conventional bonds, Islamic bonds can also be issued by the government or companies. One form of sukuk issued in Indonesia is a retail sukuk.
Menurut Financial Services Authority (OJK), retail sukuk are asset instruments issued and the sale of which is regulated by the State which is more precisely regulated by the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia. These retail sukuk can be offered or sold by selling agents (commercial banks, Islamic banks, and securities companies that have been approved by the government). OJK itself said that retail sukuk have risks that are almost the same as ORI (Retail State Bonds).
Types of Sharia Bonds
In addition to retail sukuk, bonds have several types with unique characteristics. The following are types of Islamic bonds.
Ijarah Sukuk
Ijarah sukuk sharia bonds are sukuk issued through an ijarah agreement. Thus, sukuk IIjarah is where one individual party acts independently or through a representative to lease the rights to the benefits of an asset to another party at an agreed price and rental period. This Sukuk Ijarah is not followed by a transfer of ownership from one party to another.
Musyarakah Sukuk
Sharia bonds with this type of Musyarakah sukuk, as the name suggests, are issued under a Musyarakah contract. With this agreement, a Musyarakah sukuk occurs where two or more parties cooperate to deposit or combine capital to develop a joint project or business activity. Profits and losses from the Musyarakah sukuk project will be shared by the members based on how much they participate.
Istishna Sukuk
Sharia bonds in the form of Istishna sukuk are carried out based on the Istishna agreement. An Istishna Sukuk is where there are parties who agree to make a sale or purchase transaction to finance a property or project.
Mudharabah Sukuk
Like other sukuk, Mudharabah sukuk are issued based on the Mudharabah agreement. Mudharabah Sukuk are sukuk in which there are parties who provide capital (rab-al-maal or shahibul mal) as well as parties who act in the provision of certain personnel or expertise (mudharib).
Profits from this cooperation will be shared based on the proportion (ratio) agreed in the agreement. Meanwhile, any losses that may arise will be borne by the operator of the capital, as long as the losses are not caused by the intention of the parties mudharib.
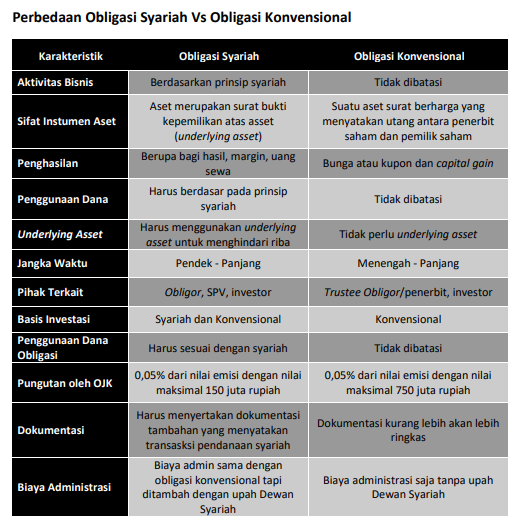
Differences between Islamic Bonds and Conventional Bonds

Islamic bonds and conventional bonds have several differences. The difference between these two types of bonds is based on the main characteristics of Islamic bonds which need to be adapted to Islamic laws. The following is an explanation of the differences between Islamic bonds and other conventional bonds.
Business Principles and Activities
The most fundamental difference between the two types of bonds – Islamic and conventional bonds – is the principle that underlies them. Sharia bonds must use sharia as a guideline for transactions as well as business activities.
Even so, the issuance of sharia bonds or sukuk itself can be carried out by non-sharia issuing bodies as long as the issuance process is in accordance with sharia.
On the other hand, conventional bonds do not have rules for specific principles in their business activities. Therefore, conventional bond issuers are not limited in their business activities.
Income Earned by Bondholders
Sharia bonds apply sharia principles in their activities. In Islam, the concept of usury – additional excess in the principal loan – is something that is forbidden or prohibited. Riba is usually found on interest instruments in investment or savings products.
That way, the income earned by Islamic bond holders may not be in the form of interest or coupons like conventional bonds but in the form of rent, profit sharing, and so on. According to the Fatwa of the National Sharia Council No. 32/DSN-MUI/IX/2002, Islamic bonds are long-term securities.
Sharia bonds must be based on sharia principles which require issuers – securities issuing companies – to pay income to bondholders in the form of profit sharing/margins/fees and pay bond funds as they mature.
Meanwhile, the income earned for conventional bondholders is in the form of interest or coupons capital gain. Where capital gain is the difference between the selling and buying prices made when selling bonds.

Underlying Assets
Conventional bonds are investment assets in the form of debt securities with interest gains for their owners. Meanwhile, Islamic bonds are assets in the form of a certificate of ownership of a company underlying assets and of course with sharia principles. Underlying assets is a financial asset that is the basis for the price of a security (in this case Islamic bonds)
Underlying assets very important for businesses with sharia principles because it avoids transactionsmoney for money' which can be categorized as usury. On the other hand, conventional bonds do not require underlying assets in the transaction.
Use of Funds
In sharia bonds or sukuk, the use of funds from the issuance of assets must be used for things that are not against sharia principles (must be something halal). Conventional bond issuance is not limited to the use of funds.
Well, that was the difference between Islamic bonds and conventional bonds. An investment asset turns out to have several different characteristics if it is adjusted to Islamic law. Are you interested in investing in bond assets?
If so, which one would you choose? Conventional or Islamic bonds? Or are you interested in other Islamic assets such as sharia mutual funds?
Header image source: Pexels
Sign up for our
newsletter
