East Ventures Exposes Indonesia's Digital Competitiveness Mapping in 2021
Riau and Bali experienced an increase in digital competitiveness ranking compared to before
East Ventures (EV) has released the second edition of the Digital Competitiveness Index (DCI) report which maps digital competitiveness in 34 provinces and 25 cities in Indonesia. This report highlights how the Covid-19 pandemic has significantly accelerated digitization in Indonesia.
One of them is the tremendous increase in internet penetration. In his report, EV-DCI stated that Indonesia's internet users increased by 25 million in just eight months (May-December 2020). Meanwhile, Indonesia took 10 years from 2009 to 2019 to get 30 million internet users to 167 million.
According to Co-Founder & Managing Partner East Ventures Willson Cuaca, Indonesia's digital economy growth will be difficult to accelerate if the infrastructure is uneven. If digital infrastructure and services are spread across every province, Indonesia can 'drive' the digital economy well.
"Just like in a slingshot, our digital economy is a ball. Because of Covid-19, our slingshot ball is stuck backwards. Here there is accumulation where startups are disciplined and respond well to situations. With infrastructure built over years and a growing internet population, the potential of our digital economy is pooled in a catapult stretch. This means that this ball will fly as soon as the Covid-19 situation subsides," he said in a virtual presentation of EV-DCI.
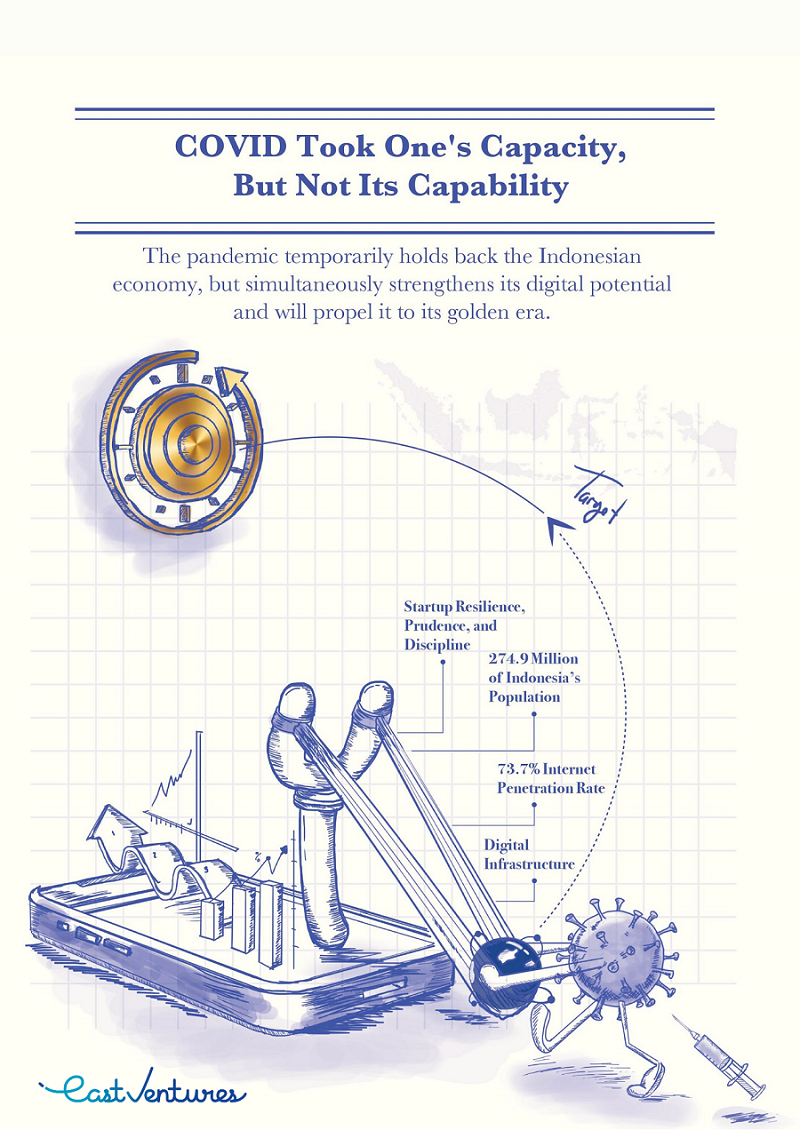
To map the digital competitiveness, EV-DCI uses measurements that refer to nine methods on three pillars, including input (human resources, use of ICT, expenditure of ICT), output (economy, entrepreneurship & productivity, employment), and supporting (infrastructure, finance, regulation & local government capacity).
Indonesia's digital competitiveness score
Overall, Indonesia's digital competitiveness index in 2021 is in the middle of 32,05, an increase from the previous score of 27,92 in 2020. There are several findings that are highlighted from the achievements of this index.
First, the score on the HR pillar is increasingly sloping from 77,3 points in 2020 to 58,4 points in 2021. This means that the competitiveness of the 34 provinces in preparing HR is more evenly distributed. On the digital infrastructure pillar, this report recorded a significant increase of up to 7,5 points from the original 46,8 points in 2020 to 54,3 in 2021.
Overall, DKI Jakarta still outperforms the province with the greatest digital competitiveness. However, this time Bali and Riau both climbed three places to fourth and seventh respectively this year. This increase was triggered by an increase in internet infrastructure that is increasingly reaching rural areas, thus encouraging business growth.
"The reason for the increase in the score in Riau is because the concentration in HR is getting better. The cooperation between Indonesia and Singapore to build the Nongsa Digital Park in Batam automatically provides spillover effects thereby driving the growth of digital talent. Likewise in Bali which is now a destination digital nomad working remote, whether in Thailand, Malaysia or other countries. That's why there is a significant economic movement there," he explained.
However, digital inequality is still very pronounced outside Java. EV-DCI reports that almost all regions of Indonesia, except Java, are represented in the ten provinces with the lowest competitiveness. There are seven non-Javanese provinces in this position, including the Bangka Belitung Islands, Lampung, Aceh, Central Kalimantan, East Nusa Tenggara, West Papua, West Kalimantan, North Maluku, West Sulawesi and Papua.
The importance of access and HR
From a number of reports highlighted above, Willson emphasized that access and human resources are an important element in increasing digital competitiveness. For example, regions open access to investment from outside.
Beyond that, there are also other variables that can encourage digital competitiveness per region, such as the development of education and capabilities. Willson considers that digital absorption of MSMEs can be faster if every region in Indonesia has good human resources. That is, there is an acceleration that makes output become bigger.
"Digital equity is not related to having a startup in every region. Startups must be concentrated in big cities like Jakarta, but they can open branches without having to wait for new startups in that area. What is built in Jakarta can be used elsewhere, that's why the road has to be built so it can be fast and enjoyable," explained Willson.
Impact of the pandemic
Transportation and travel online These are the two sectors that have been significantly affected by Covid-19. This impact can be seen from the number of visits as of January 2020 which reached 1,29 million visits, dropping 89% to 141.269 as of January 2021.
However, changes in the pattern of Indonesian society to domestic travel is predicted to boost the OTA business by five times in 2025. Especially with wider vaccine distribution, confidence level towards the OTA business will slowly recover.
On the other hand, positive impacts were also experienced in other sectors, such as digital infrastructure, E-commerceand EdTech. In the case of Tokopedia, unicorn This pocketed 2,5 million merchants throughout 2020. In fact, it took Tokopedia 10 years to get 7 million merchants.
"All businesses are forced online because I can't sell offline during a pandemic. That's why the spending of pulses also increases. In Indonesia, there are 30 million new internet users who make transactions on the Internet for the first time E-commerce during the pandemic. But, is it after go online, the digital economy can immediately accelerate? Here's why O2O is important. Behavior will remain stay, once the vaccine is distributed, offline and online road, acceleration will be faster," he said.
The next digital trend
More Coverage:
Willson also revealed some of the next digital trends that will be accelerated due to Covid-19. First, sectors related to media (games, social media, video, etc.) will increase and encourage the creation of a new category, namely creator economy.
"Everyone can create their own content in the future in line with the trend of consumer behavior moving away from TV [consumption]. Eyeball everything was on TV, now consumers can [create] content following market trends," said Willson.
Next up is the trend of investing in digital wallets. According to him, the digital wallet business has dominated the Indonesian market. When it comes to investing in digital wallets, this trend is considered no longer attractive. "What is interesting is how the contents of the wallet are. Hence, all [startup players] go to digital banks," he said.
Lastly, concept working remotely and Work From Home (WFH), which companies are getting used to during the pandemic, will further increase the adoption of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), for example cloud based computing.
Sign up for our
newsletter
